- Introduction: An Unexpected Journey
- Initial Assessment of Dental Trauma: First Steps
- Immediate Care: How to Minimise Damage
- When to See a Dentist: Timing Matters
- Possible treatments for dental trauma
- Prevention: Better than Cure
- Conclusion: Oral Health in Your Hands
- Scientific references
Introduction: An Unexpected Journey
One fine spring afternoon, while João was enjoying a game of football with friends, a moment of distraction changed everything: an unexpected shock, a muffled scream and a sharp pain. João had just experienced what many fear: dental trauma. As he hurried to the nearest mirror, questions began to form in his mind. “What do I do now?” This is the starting point of our journey through urgent care in the event of dental trauma.
Initial Assessment of Dental Trauma: First Steps
In the immediate aftermath of dental trauma, the spectrum of first aid actions varies widely depending on the nature of the damage suffered. In addition to avulsion, teeth can suffer fractures, dislocations or injuries to adjacent soft tissues. Each scenario requires a careful approach to minimise damage and maximise the chances of recovery.
For fractured teeth, it is vital to collect and preserve the tooth fragments if possible. These can be packed in milk or saline solution, similar to the procedure for avulsed teeth, and taken to the dentist to assess the possibility of reconstitution. In cases of fracture, avoiding exposing the tooth to extreme temperatures and eating hard foods can prevent further damage until a professional assessment is possible.
In situations of luxation, when the tooth is dislocated but not completely avulsed, it is recommended to avoid contact or pressure on the affected tooth. Not trying to realign the tooth manually can prevent damage to the periodontium and surrounding tissues. Applying a cold compress to the cheeks can help reduce swelling and discomfort.
Soft tissue injuries, such as cuts or lacerations to the gums, tongue or cheeks, require care to prevent infection. Gently cleaning the area with warm water and applying direct pressure with sterile gauze can control bleeding. If the bleeding does not stabilise or if the injury is deep, seeking medical attention is essential.
Immediate Care: How to Minimise Damage
The first hour after the incident is critical. The recommendation is to clean the avulsed tooth with water and try to replace it in the cavity, always handling it by the crown. Research published in Dental Traumatology (2020) shows that the likelihood of successful reimplantation of an avulsed tooth is significantly higher when carried out within the first 60 minutes.

Quando Procurar um Dentista: O Tempo Importa
O timing para procurar atendimento odontológico é crucial. Uma revisão sistemática da literatura, destacada no Journal of Endodontics, sublinha a importância de receber cuidados dentários especializados dentro de 2 a 4 horas após o trauma, para otimizar os resultados do tratamento.
Tratamentos Possíveis para Traumas Dentais
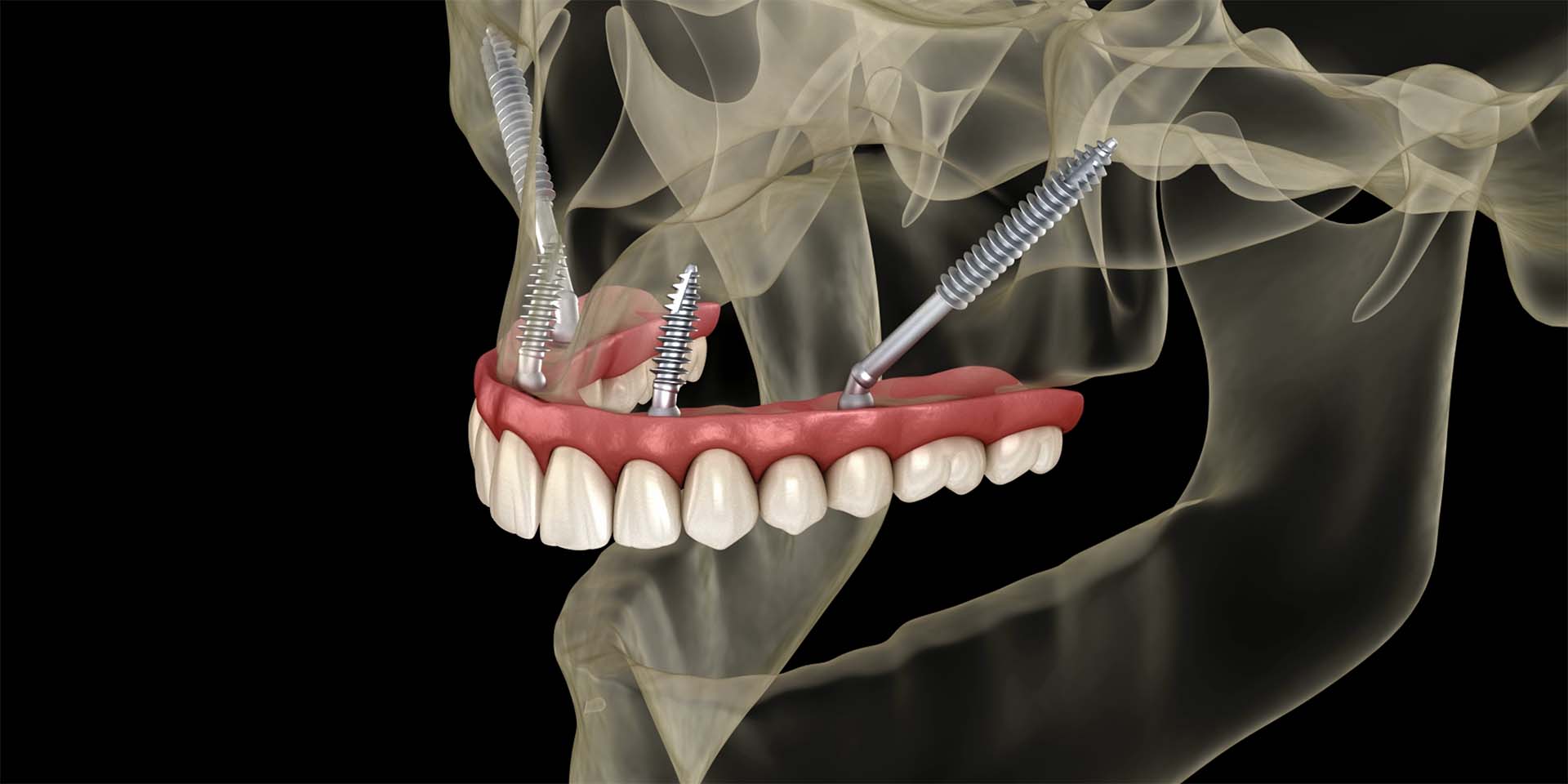
Os tratamentos variam conforme o tipo e a severidade do trauma. Vão desde a simples reimplantação do dente até procedimentos mais complexos como o tratamento de canal ou a colocação de implantes dentários. Estudos do Journal of Oral Rehabilitation apontam que a escolha do tratamento adequado é determinante para a recuperação funcional e estética do dente afetado.
Prevenção: Melhor do que Curar
Adotar medidas preventivas pode ser a chave para evitar traumas dentais. Uso de protetores bucais durante atividades desportivas e evitar hábitos nocivos, como o uso dos dentes para abrir objetos, são estratégias eficazes recomendadas pela World Dental Federation.
Conclusão: A Saúde Oral nas Suas Mãos
A história do João termina com um final feliz, graças à sua rápida ação e ao cuidado especializado que recebeu. Este episódio serve de lembrete da importância de estar preparado para agir de forma adequada frente a um trauma dental. Lembre-se, a saúde oral está, literalmente, nas suas mãos.
E agora, já sabe o que fazer se enfrentar uma situação semelhante?
Scientific references:
- American Association of Endodontists. “Saving Your Natural Teeth.” AAE, 2023.
- Andersson, L. et al. “International Association of Dental Traumatology guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries: Avulsion of permanent teeth.” Dental Traumatology, vol. 36, no. 4, 2020, pp. 331-342.
- DiAngelis, A.J. et al. “Guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries: 1. Fractures and luxations of permanent teeth.” Journal of Endodontics, vol. 42, no. 9, 2016, pp. 1-25.
- Petti, S. et al. “Prevention of traumatic dental injuries: Knowledge and behaviors of schoolchildren.” Journal of Oral Rehabilitation, vol. 44, no. 3, 2017, pp. 163-168.
- World Dental Federation. “Sports Dentistry: Minimizing the Risk of Sports-Related Oral Injury.” FDI, 2021.