- Introduction: A Journey to the Perfect Smile
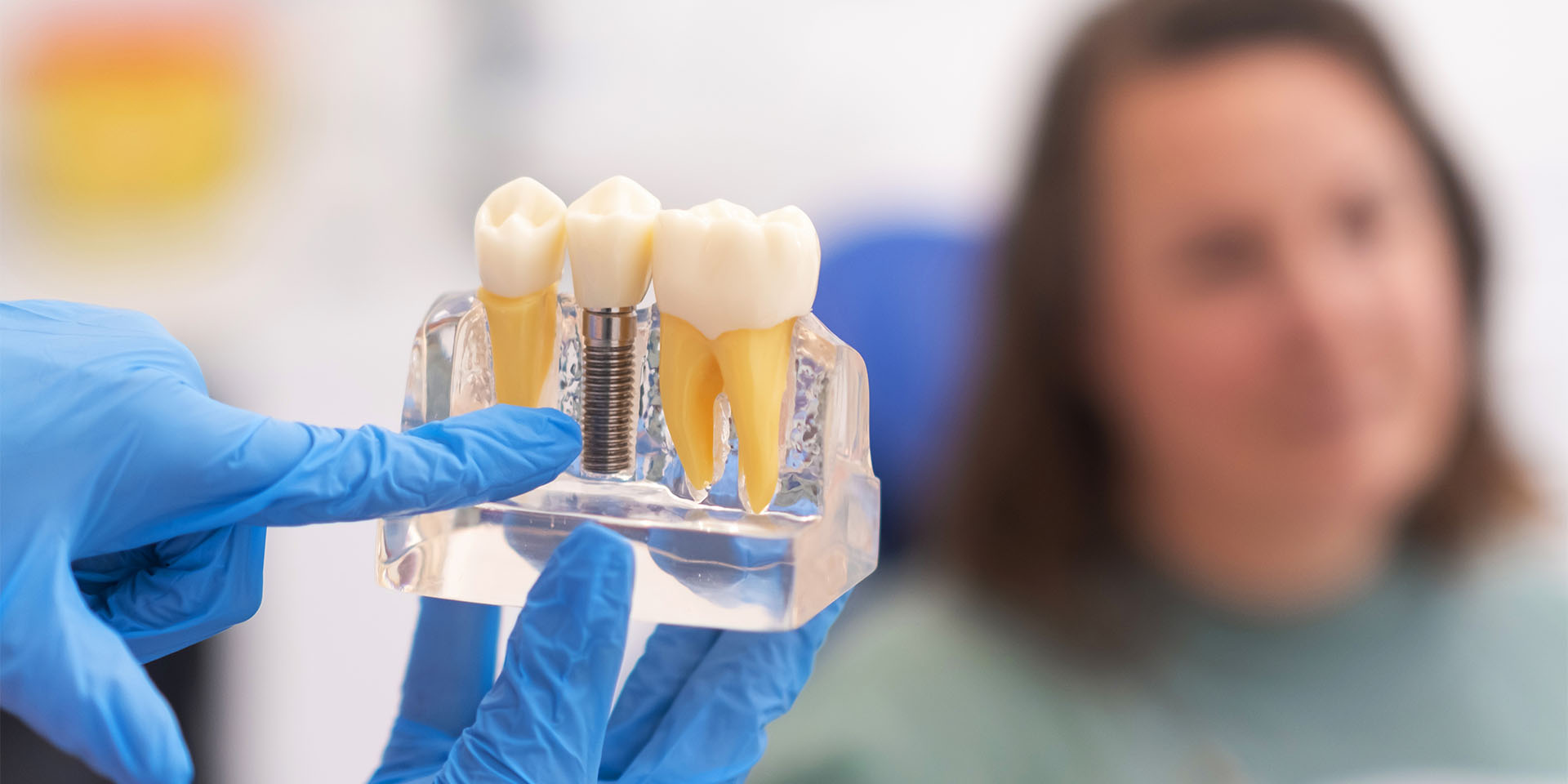
- What Are Dental Implants?
- The Science Behind Implants: Osseointegration
- The Implementation Process: Step by Step
- Post-Implantation Care and Maintenance
- Dental Implants and Smile Transformation
- Conclusion: A bright future for dental implants
1 Introduction: A Journey to the Perfect Smile
At the forefront of modern dentistry, dental implants represent a revolution in both the recovery of masticatory functionality and smile aesthetics. Evidencing their relevance, statistics point to a continuous increase in the global demand for dental implants. In Portugal, this market is growing, reflecting a global trend and highlighting the importance of these dental solutions.
2. What are Dental Implants? – Expansion with Different Types of Implant Systems
Dental implants are not limited to a single form or technique. There are several implant systems developed to meet different patient needs. Here is a detailed description of some of the most common implant systems:
Implants All-on-4:
- Description: The All-on-4 system uses four implants to support a complete fixed arch prosthesis. It is a solution for patients with significant tooth loss.
- Advantages: Allows the replacement of all upper or lower teeth with just four implants, reducing the need for bone grafts.
- Procedure: The implants are placed at specific angles to maximise the use of existing bone.
All-on-6 implants:
- Description: Similar to All-on-4, but with six implants to support the dental prosthesis.
- Advantages: Offers greater stability and load distribution, especially in cases where there is greater bone density.
Implant-supported bridges:
- Description: An implant-supported bridge is used to replace several teeth. This bridge is anchored to implants instead of natural teeth.
- Advantages: Offers a more stable and durable alternative to traditional bridges, avoiding the need to wear down adjacent teeth.
Single implants:
- Description: Used to replace a single missing tooth. An implant is placed in the bone, followed by the crown.
- Advantages: Maintains the integrity of the bone and adjacent teeth, preventing displacement of neighbouring teeth.
Implant-supported overdentures:
- Description: An overdenture is a removable prosthesis that is supported and retained by implants.
- Advantages: Provides greater stability than conventional dentures, improving chewing function and comfort.
Immediate Loading Implants:
- Description: Also known as “same-day teeth”, they allow the placement of a crown or temporary prosthesis immediately after the implant is inserted.
- Advantages: Reduces treatment and recovery time, allowing patients to leave with functional teeth on the same day as surgery.
Each of these systems has its own specific indications and advantages. Choosing the most suitable implant system for a patient depends on several factors, including the quantity and quality of bone available, the patient’s general health and aesthetic and functional needs. A careful assessment by a specialised dentist is essential to determine which implant system is the most appropriate for each individual case.
3. The Science Behind Implants: Osseointegration
The success of dental implants depends crucially on the process of osseointegration, where the implant fuses to the jawbone. This process is essential for the stability and longevity of the implant. Globally, the growing need for dental prostheses and the greater adoption of preventive and restorative dental care are driving the popularity of implants.
4. The Implementation Process: Step by Step
The implantation of a dental implant is a carefully planned and executed process that takes place in several crucial stages. Here is a detailed step-by-step guide:
Initial Assessment and Planning
- Dental Consultation and Examination: The first step is a comprehensive consultation, where the dentist assesses the patient’s oral health. This may include X-rays or CT scans to examine the bone structure.
- Treatment planning: Based on the examination, the dentist develops a personalised treatment plan. This plan takes into account factors such as the location of the missing tooth and the amount of bone available.
Preparing the Implant Area
- Tooth Extraction, if Necessary: If there is a damaged tooth that needs to be removed, this is done first.
- Bone preparation: In some cases, a bone graft procedure may be necessary to strengthen the jawbone.
Implant placement
- Implantation surgery: Carried out under local anaesthetic, the titanium implant is carefully inserted into the jawbone. The implant serves as a new root for the tooth.
- Healing and Osseointegration: After the implant is inserted, a healing period begins, which can last several months. During this time, osseointegration takes place, where the bone fuses to the implant.
Abutment placement
- Installing the Abutment: Once the implant is integrated into the bone, an abutment is placed over it. This abutment will support the new crown.
Placement of the Dental Prosthesis (Crown)
- Moulding and Crown Creation: Dental impressions are taken to create a crown that fits perfectly in the patient’s mouth and matches the adjacent teeth.
- Crown placement: Finally, the crown is fixed to the abutment, completing the dental restoration process.
Monitoring and Maintenance
- Follow-up appointments: Follow-up appointments are essential to ensure the proper health and functionality of the implant.
- Maintenance Care: Detailed instructions are provided on how to care for the implant, including proper oral hygiene and regular visits to the dentist.
Each of these steps is vital to ensuring the long-term success of the dental implant. It’s important to note that the duration and complexity of the process can vary depending on the patient’s individual needs and the specifics of the case.
5. Post-Implantation Care and Maintenance
Proper maintenance is vital for the longevity of dental implants. The growing global awareness of the importance of oral hygiene and regular care for dental implants is reflected in the increased demand for post-implantation maintenance and follow-up services.
6. Dental Implants and Smile Transformation
Dental implants have a significant impact on patients’ self-esteem and quality of life. Demand for aesthetic procedures such as implants is robust, with Portugal emerging as a popular destination for dental tourism, offering high-quality treatments at affordable prices compared to other countries.
7. Conclusion: A Bright Future for Dental Implants
Dental implants represent a promising future in dentistry. The growing demand for aesthetic and preventive treatments, together with the increase in the elderly population, is driving the dental implant market, both in Portugal and globally.
Bibliography:
https://www.globaldata.com/
https://www.researchandmarkets.com/
https://www.dentaltown.com/